Solid substance
Solid substance – In everyday life, we are not free from the substances in our lives. Like liquid ,solid and gas. For example, is frozen water, which is one example of the liquid turns solid.
On this occasion YukSinau.co.id will discuss solid matter, let's look at the complete explanation of the material below.
Table of Contents
Understanding Substance
Substance is something that occupies a space and has mass. In every object consists of substances or commonly called matter. Substances divided into 3 based on its shape, namely liquid, solid, and gas.
Understanding Solid Substances
Something that has matter or substance that has the form and volume that occupies a certain space is called a solid substance. This substance is formed in two main ways how the substance can be formed, i.e, arranged from neatly organized lines or randomly arranged.
Solid substances which are arranged randomly are called amorphous. Generally, Amorphous has a shiny and elastic texture and appearance.
An example is: candle, rubber,and plastic
Solid substances whose particles are neatly arranged are called crystals. Examples of crystals namely: diamond, ice Cube, salt and metal.
Properties of Solids
- Has a fixed volume.
- Having a regular and tight molecular arrangement.
- Has a very strong attractive force.
- Has a fixed form.
- Its shape does not change to follow the container it occupies.
- The shape of the movements vibrate and spin in place.
- It has molecules that do not move freely and are not easily separated.
Characteristics of Solid Substances
| 1 | Volume | Permanent |
| 2 | Volume | permanent |
| 3 | Particle motion | Not free |
| 4 | Place the particles | Nearby |
| 5 | Arrangement of particles | Very close |
| 6 | Particle style | Very strong |
| 7 | Can't compress |
One characteristic of this one substance is that its shape and volume are fixed. An example is a box-shaped beam. If we try to move the block in a container that is different in shape, then the block will remain square.
So it is with the volume of the beam, the volume on the beams will not change even in containers of different shapes.
That is because of that has a very strong attraction between particles.
Pressure
Pressure is a magnitude of the force acting on an object per unit area of pressure.
Pressure is formulated as follows:
P=F/A
Information:
P = pressure (Well)
F = Tell (N)
A = area wide ( m2 )
The more the style is given, then the pressure generated will increase.
Expansion
Increasing the size of an object because of a change in temperature or because it receives heat is called expansion. Expansion occurs 3 was sitting, that is fall, solid, and gas.
Expansion Formula
For expansion in solids there is 3 formula including the one below:
1. Broad Expansion
Broad expansion is an expansion that will increase the area of an object due to an increase in temperature. Broad expansion can occur on thin broad objects such as metal plates.
Broad expansion can be formulated as follows:
| A = A0 + A0 α . ΔT A = A0 (1 +α . ΔT ) |
Information:
A = The area of the object after expanding (m)
A0 = Area of the item before expanding (m)
α = coefficient( /0C )
ΔT = temperature change on the object(C0 )
2. Volume expansion
Volume expansion is expansion which causes an increase in volume due to increased temperature.
Volume expansion can occur with objects that have a volume that cannot be ignored, such as metal in the shape of a box.
| V = v0 + V0 α . ΔT V = v0 + (1 +α . ΔT ) |
Information:
V = Volume of the object after expansion (m)
V0 = Volume of the object before expanding (m)
α = coefficient ( /0C )
ΔT = temperature change on the object (C0 )
Information:
A = The area of the object after expanding (m)
A0 = Area of the item before expanding (m)
α = coefficient( /0C )
ΔT = temperature change on the object(C0 )
3. Long Expansion
Long expansion is expansion which will increase the size of an object to be longer than the previous size due to an increase in temperature.
Length expansion can be formulated as follows :
| L = L0 + L0 . α . ΔT L = L0 (1+ α . ΔT ) |
Information:
L = Length of the object after expanding (m)
L0 = Length of the object before expanding (m)
α = coefficient ( /0C )
ΔT = temperature change on the object (C0 )
Difference in Solid Substances, Liquid substances, and Substance Gas

| Nature | Liquid substances | Gas substance | Solid substance |
| Volume | Permanent | it depends the place |
Permanent |
| Compression Mass Type |
Difficult to compressed |
Easy to compress | Can't compress |
| Shape | follow container shape which is occupied |
Following the shape the container it occupies |
Permanent |
| Mass Type | Is | Small | Big |
In solid matter it has a certain volume and shape. The substance has a very compact particle distance. In this substance the particles move freely.
The liquid substance has a certain volume, but the form it has is not fixed, liquid has a form that depends on the shape of the container it occupies. Liquid substances have a spacing between particles that are more tenuous. And particles that are in liquid form can move freely but are limited.
Volume and shape on this can change. In this the distance between the particles is tenuous and the particles can move freely.
Examples of Solids
- Wood
- Stone
- Aluminum
- Metal
- Diamond
- Diamond
- Glass
- Iron
- Candle
- Bone
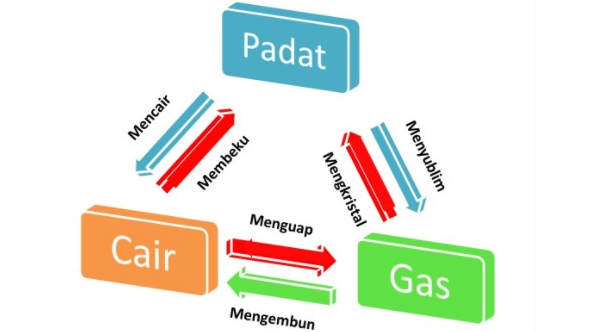
Substance Change
In physics there are several changes to the substance as below :
- Froze up, freezing is a change in the shape of a liquid into a solid.
Example : cold water will turn into ice cubes - Yawn, Yawning is a form of change in liquid into gas.
Example: heated water - Replied, is a form of conversion of solid matter into gas. Example: camphor
- Melt, melting is a form of change of a solid into a liquid
Example: candle. - Condense, condensation is a form of conversion of a gas substance into a liquid.
Example: dew - Crystallized, crystallized is a form of change in the form of gas into solid.
Example: kristal.
This is a complete discussion of Solids, hopefully can be useful for Physics learning materials. To find out other Physics material, please visit the following article.
Other Articles :
- Gauss's Law
- Lenz's Law
- Electromagnetic wave
- Black Body Radiation
- Potential Energy Formula
- Unidirectional Electric Current
The post Zat Padat appeared first on YukSinau.co.id.
