Differences in the Structure of DNA and RNA
What is the difference between DNA and RNA? What is the difference between the structure of DNA and RNA?? What is the function of DNA and Rna? DNA (Deoxyribo Nucleic Acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid; ribose nucleic acid) is a polymer of nucleotides linked by chains by means of phosphodiester bonds. For a complete explanation, see our discussion of the differences in complete DNA and RNA structures below.
Table of Contents
Differences in the Structure of DNA and RNA
DNA (Deoxyribo Nucleic Acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid; ribose nucleic acid) are polymers of nucleotides linked by chains by means of phosphodiester bonds.
In biological systems, DNA and RNA act as information carrier molecules or as catalysts in some RNA molecules. This brief review will focus on various aspects of the differences in the structure of DNA and RNA. For more details, please see the material below!
DNA structure
Genes consist of a nucleic acid called deoxyribonucleic acid (deoxyribonucleic acid). In addition to various types of viruses, Molecules act as carriers of genetic information in all organisms (Genetics, 2007: 53).
These acids are polymers consisting of deoxyribonucleotide molecules linked together to form long polynucleotide chains..
This long DNA molecule is formed by bonds between C-numbers 3 and C-number 5 on the deoxyribose molecule through the phosphate group (Basic Biochemistry, 2006: 135).
DNA is a polymer. DNA recombination is a natural process in which the genetic material elements (DNA polymer fragments) combined to form another DNA molecule. The product DNA is referred to as recombinant DNA. (Fessenden, 1982)
Chemically, DNA contains the following properties:
- Has a deoxyribose sugar group.
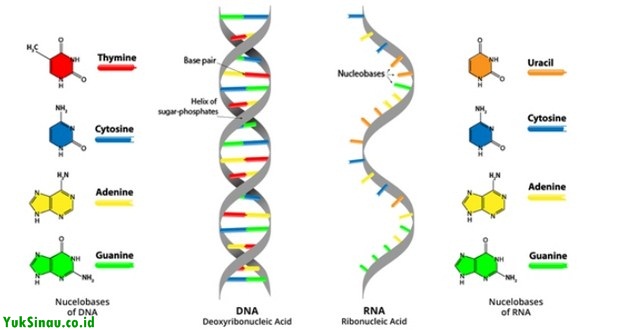
- The nitrogenous base is guanine (G), cytosine (C), mine (T) and adenine (A).
- Has an anti parallel double helix chain
- The content of nitrogen bases between the two chains is the same and in specific pairs with each other. Guanine always pairs with cytosine (G±C), and adenine and adenine pair with thymine (A – T), So the amount of guanine always equals the amount of cytosine. Likewise adenine and thymine.
Structure of RNA
Asam ribonukleat (ribonucleic acid, RNA), is wrong 1 from 3 major macromolecules (other than DNA & protein), which has an important role in all forms of life (Key, 1976: 463).
Ribonucleic acid carries the genetic material and plays an important role in genetic expression.
In the central dogma of molecular genetics, RNA mediates between information transmitted/carried by DNA and phenotypic expression embodied as protein (Key, 1976: 463).
RNA consists of polybonucleotide chains, whose base is usually guanine, adenine, uracil, and cytosine. RNA is found in the nucleus and in the cytoplasm of cells. There is more variation in the form of RNA than DNA.
RNA has a molecular weight 25.000 up to several million. Most of the RNA contains a single polynucleotide chain, but this chain can be folded to form a region of the double helix containing an A base pair: U & G.
There are three main types of RNA, namely transfer RNA (tRNA), messenger RNA (mRNA), and ribosomal RNA (rRNA) .
RNA plays a role in the disclosure of genetic information. tRNA (Mr25,000) act as adapters in the synthesis of polypeptide chains. tRNA includes 10-20 percent of the total RNA in the cell.
There is at least one type of tRNA for each type of amino acid. tRNA has a relatively high nucleoside content. This nucleoside can be said to have a unique structure, for example adenine, cytosine, guanine and uracil / steel plate (Ngili, 2013: 307-308).
The basic structure of RNA is similar to DNA. RNA is a polymer consisting of a number of nucleotides. Each nucleotide has a phosphate group, pentose groups and nitrogenous base groups (bass N).
Polymers consist of intermittent bonds between the phosphate group of one nucleotide and the pentose group of another nucleotide..
Ribonucleic acid is a polymer consisting of ribonucleotide molecules. Ribonucleic acid is formed by bonds between the number C atoms 3 and C atoms 5 on the ribose molecule via a phosphate group (Poedjiati, 2006: 138).
DNA carries the genetic code, but it is actually the RNA that “translates” the code becomes protein synthesis.
The structure of RNA is similar to the structure of DNA. series of sugar units (in this case ribose) linked together by phosphate bonds.
Each sugar is bound to a base. The main base in RNA is adenine, guanine, sweet, and uracil (not thymine).
Uracil forms the preferred hydrogen bonds (which corresponds to the hydrogen bonds in thymine) and is always paired with adenine in RNA synthesis.
Messenger RNA (mRNA) synthesized under “instructions” DNA. The mRNA molecule is smaller than the DNA molecule.
In the synthesis of mRNA molecules, only part of the DNA spiral unravels, then the complementary ribonucleotides are aligned and then polymerized.
After polymerization, an mRNA molecule with a DNA molecule does not form a Sprila with a DNA molecule. Otherwise, it leaves the nucleus of the cell to support protein biosynthesis. (Fessenden, 1982)
Difference between DNA and RNA
Although there are many similarities with DNA, RNA is different from DNA. What is the difference between DNA and RNA?
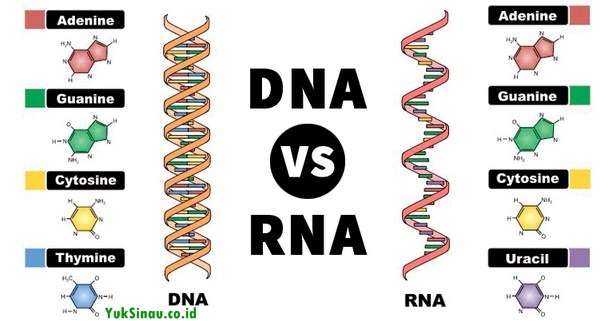
- DNA is in the cell nucleus and RNA is in the cell nucleus, ribosome, cytoplasm.
- The pentose portion of RNA is ribose, while the pentose portion of DNA is deoxyribose.
- The shape of the DNA molecule is a double helix, whereas the shape of the RNA molecule is not a double helix
- The amount of guanine in an RNA molecule is not necessarily identical to that of cytosine, so that the amount of adenine does not have to be identical with that of uracil
- RNA contains purine bases, guanine, adenine, and cytosine like DNA but no thymine. Otherwise, RNA contains uracil. So, The pyrimidine bases of RNA are different from the pyrimidine bases of DNA.
Differences in the Structure of DNA and RNA
- RNA differs structurally from DNA in that it consists of ribose as a pentose sugar & uracil as a pyrimidine group. Ribonucleic acid is not a double helix, but Deoxyribo Nucleic Acid forms the same helical structure, with base pairs. As in DNA, the bases in this region of the helix are hydrogen bonded to the RNA.
- RNA is present as a single helix in most regions. The pentose sugar in RNA is ribose and DNA is deoxyribose. Deoxyribose does not have an oxygen atom on it 5 "Carbon from ribose sugar.
- In RNA, thymine is replaced by uracil, which binds to adenine to form a helical structure.
- Structurally, DNA is a more compact molecule with a certain height, wide, and large groove dimensions & small.
Differences in the Functions of DNA and RNA
Based on its function, DNA acts as the genetic material that is passed down to generations. RNA acts as a mechanism for carrying/transporting the information that the body goes through in producing fully functional proteins.
Based on its function, DNA acts as the genetic material that is passed down to generations. RNA acts as a mechanism for carrying/transporting the information that the body goes through in producing fully functional proteins.
DNA (Deoxyribo Nucleic Acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid; ribose nucleic acid) are polymers of nucleotides linked by chains by means of phosphodiester bonds.
In biological systems, DNA and RNA act as information carrier molecules or as catalysts in some RNA molecules.
Genes consist of a nucleic acid called deoxyribonucleic acid (deoxyribonucleic acid). In addition to various types of viruses, Molecules act as carriers of genetic information in all organisms (Genetics, 2007: 53).
These acids are polymers consisting of deoxyribonucleotide molecules linked together to form long polynucleotide chains..
This long DNA molecule is formed by bonds between C-numbers 3 and C-number 5 on the deoxyribose molecule through the phosphate group (Basic Biochemistry, 2006: 135).
DNA is a polymer. DNA recombination is a natural process in which the genetic material elements (DNA polymer fragments) combined to form another DNA molecule. The product DNA is referred to as recombinant DNA. (Fessenden, 1982)
Chemically, DNA contains the following properties:
Has a deoxyribose sugar group.
The nitrogenous base is guanine (G), cytosine (C), mine (T) and adenine (A).
Has an anti parallel double helix chain
The content of nitrogen bases between the two chains is the same and in specific pairs with each other. Guanine always pairs with cytosine (G±C), and adenine and adenine pair with thymine (A – T), So the amount of guanine always equals the amount of cytosine. Likewise adenine and thymine.
Thus our discussion of the Paper Material Differences in the Structure of DNA and RNA. Read it too Centrosome function. May be useful.
The post Differences in the Structure of DNA and RNA appeared first on YukSinau.co.id.
