Atmospheric Layer
Layers of the Atmosphere and Their Explanation – What is Atmosphere? What is the function of the layers of the Atmosphere? What are the characteristics of the layers of the Atmosphere? What are the benefits of Atmosphere ? If this is the question, friend Yuksinau.co.id. Then consider our explanation of the Atmospheric Layers Paper Material and its Explanation, includes Definition, Atmospheric Scope, Features Features, Function, Structure and Figure Below.
Table of Contents
Understanding the Atmosphere
Etymologically, atmosphere comes from the word “atmosphere,” which means air, and “ball,” which means layers.
So the atmosphere is a layer of air or gas that surrounds the earth, while air means all gases consisting of various odorless substances, has no color, and invisible. The atmosphere is the outermost layer of the earth's crust below the lithosphere (Sardiman et al, 2004: 20).
Other definitions, the atmosphere is the layer of gas that covers/encloses a planet from its surface into space. On earth, atmosphere from 0 km above ground level to 560 km.
Earth's atmosphere is composed of various gases with different compositions. Gas nitrogen (78,08%) and oxygen gas (20,95%) are the two types of gas with the largest composition.
The atmosphere is not only made up of different gases, but also from several layers with different functions.
Read Also : Biosphere Phenomenon
Atmospheric Scope
Earth's atmosphere consists of 20 gas type. The two main gases are oxygen and nitrogen. The atmosphere contains some water and dust particles because the Earth's atmosphere is a very large area of air, which naturally has weight.
If the atmosphere can be used by placing it on a scale, then it weighs approx 5.700.000.000.000.000 (5.700 trillion) ton.
1. Air consists of various constituent substances, and has its own number, as for the forming substance namely :
- Nitrogen 78%
- Oxygen 21%
- Argon 0,9%
- Carbon dioxide 0,03%
- Carbon, hydrogen, neon, xenon, helium, and ozone by 0,07%.
2. Physical properties of the atmosphere, atmosphere that surrounds the earth, has the following characteristics:
- Transparent to some types of radiation
- Elastic and dynamic, so that it can expand and also shrink
- Colorless, odorless and cannot be felt
- Heavy, so it can be stressful
- Consists of several gases
- Consists of several layers
Layers of the Atmosphere and Their Explanation
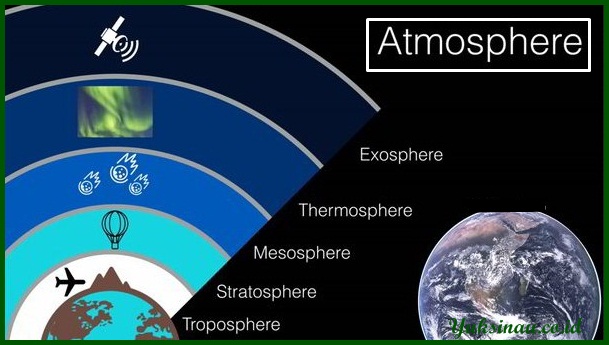
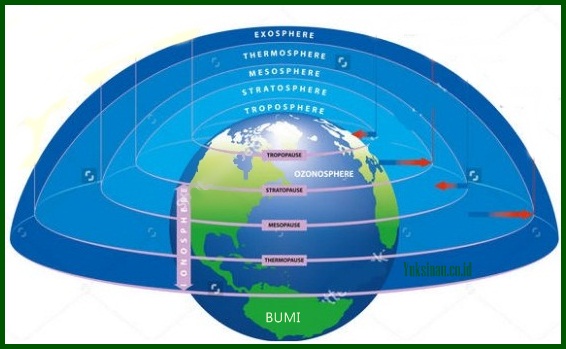
The atmosphere has a structure of air layers starting from the closest to the most distant, This layer is the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, exosphere, and the thermosphere. Then what do you mean by layers. Nah, The following are the layers of the atmosphere and their explanation :
1. Troposper (9-12 km)
Troposphere layer, is the layer of air that is closest to the surface of the earth but with a different thickness, that is 9 km in the polar region and 12 km in the equatorial region (Katino, 2006: 31).
The characteristic of this layer is that every time we go up 100 meter, air temperature dropped from 0,5 Becomes 0,64 ° C.
A thick layer of air in the troposphere protects the earth from sunlight, so that the Earth's temperature is not too high during the day and not too low at night.
On this layer, air movement process (wind) going on, cloud formation and rain, which is a feature of weather elements. Weather has a huge impact on life on earth.
2. Stratosphere (12-50 km)
The stratosphere is the layer of air around 18 to 60 km above the earth's surface (Katino, 2006: 31).
On this layer, at a height of approx 22 km, Ozone concentration is used to protect the troposphere from solar radiation / ultraviolet.
In the stratosphere, the process of compounding and transferring heat occurs so that the stratosphere has a layer of the mesosphere. The boundary between the traposphere and the stratosphere is called the maximum temperature of the tropopause, while the boundary between the stratosphere and mesosphere is called the stratopause, which coincides with the ozone portions at maximum temperature.
3. mesosphere (50-80 km)
The mesosphere is the layer that lies above the stratosphere (Katino, 2006: 31).
This layer plays a role in reflecting radio and television waves (VHF & UHF). This layer protects the earth from meteor showers.
At the top, the air temperature in the mesosphere becomes colder. In the mesopause layer (the middle layer between the mesosphere and thermosphere) temperature can reach 140˚C below zero (-140˚C)
4. Thermosphere (50-80 km)
The thermosphere is the warmest layer of the atmosphere compared to the other layers of the atmosphere (Katino, 2006: 31).
This layer is located at the height 80 km to the boundary between the outer atmosphere. Temperature up 1.500 ° C can occur in this thermosphere. In this layer is the ionosphere layer (height 80-450 km).
The ion particles generated in this layer reflect longwave and shortwave radio waves.
5. Exosphere Layer
It's called the exosphere, because it is the outermost layer of the atmosphere, where the influence of gravity is so low that air collisions are unlikely to occur. The height of this layer is between 500 kms and 1.000 km.
The gas grains in this layer gradually escape into space. This layer is also called Dissipasisphere.
Read Also : Map of the Distribution of Flora and Fauna
Everything in this world certainly has its own role or function, the same goes for the atmosphere, where the atmosphere has a very important function or role for the earth. What is the function of the Atmosphere?
- The atmosphere is an important source of gases used in the life processes of living things on Earth. Oxygen, for example, is a gas that is very important for human life and other living things on Earth. Likewise, carbon dioxide (CO 2) and nitrogen (N 2) contained in the atmosphere is indispensable for the processes of plant life on Earth.
- The atmosphere acts as a filter for solar radiation. ozone layer (O3) in the atmosphere block sunlight, which can damage the organs of the body or even kill living things on earth.
- The atmosphere is the buffer temperature for the earth's temperature. The gases in the atmosphere and water vapor absorb and reflect the received radiation. The buffering process by the atmosphere supports the stability of the temperature on earth so that the temperature on earth does not get too hot during the day and not too cold at night.
- The atmosphere regulates the maintenance of weather and climate processes on Earth. Part of the hydrologic cycle (cloud formation and rain), which is a very influential factor for the weather and climate on Earth, occurs in the Earth's atmosphere.
If the earth had no atmosphere, many life processes will be disrupted. No oxygen in the atmosphere, living things cannot survive.
No filtering of solar radiation in the atmosphere, the plains of the earth will sink, because all the ice at the poles of the earth will melt.
Without buffering process by the atmosphere, Earth's temperature can reach 93 ° C during the day and -184 ° C at night.
Characteristics of the Layers of the Atmosphere
The atmosphere has certain layers which of course have their own characteristics or characteristics. Then what are the characteristics of each layer of the atmosphere? Nah, The following are the characteristics of the layers of the Atmosphere :
1. Troposphere
- Generally, this layer is the thinnest with a thickness of approx 12 km from the ground
- The height of the troposphere varies from place to place. In the polar regions the altitude is approx 8 km and the equatorial area or the equatorial area can reach 16 km.
- Is the layer that is directly related to the surface of the earth and as a place to live for species of living things.
- Where weather and climate events occur, eg rain, wind, lightning, and clouds.
- There is a tropopause layer, which is the layer between the troposphere and the stratosphere.
- For each increase 100 meter, the temperature drops 0,5 to 0,6 ° C.
2. Stratosphere
- Layers that have a height of approx 12-60 km.
- Temperature increases with increasing altitude, ie from -60 ° C (of tropopause) the 10 ° C at its peak.
- There is an ozone layer that functions to protect the earth from exposure/ultraviolet radiation from the sun by means/its properties that absorb excess rays or light. This absorption of solar radiation by ozone causes air temperature to increase with each increase in altitude
- Does not contain moisture, clouds or dust, the air is dry
- Ada stratopause layer, which is the layer between the stratosphere and the mesosphere
3. mesosphere
- Stands about 60-80 km.
- The temperature -50 ° C and -70 ° C.
- Is a layer that protects the earth from meteors and other celestial bodies that fall to earth. Meteors burn and break when the layers reach this layer and become small fragments called meteorites.
- There is the mesopause layer which is the layer between the mesosphere and thermosphere
4. Thermosphere
- Stands about 80-800 km.
- This layer is often referred to as the hot layer.
- The air temperature at the top of this layer can reach> 1000 ° C.
- There is also an ionosphere layer in this layer.
- The ionosphere layer functions to spread radio waves
5. exosphere
- Height over 800 km
- The outermost layer of the atmosphere, So the influence of gravity is very low
- The gas content of the atmosphere is also very low
Read Also : Environmental Benefits
Etymologically, atmosphere comes from the word “atmosphere,” which means air, and “ball,” which means layers.
So the atmosphere is a layer of air or gas that surrounds the earth, while air means all gases consisting of various odorless substances, has no color, and invisible. The atmosphere is the outermost layer of the earth's crust below the lithosphere (Sardiman et al, 2004: 20).
Other definitions, the atmosphere is the layer of gas that covers/encloses a planet from its surface into space. On earth, atmosphere from 0 km above ground level to 560 km.
Tropospheric Characteristics :
1. Generally, this layer is the thinnest with a thickness of approx 12 km from the ground
2. The height of the troposphere varies from place to place. In the polar regions the altitude is approx 8 km and the equatorial area or the equatorial area can reach 16 km.
3. Is the layer that is directly related to the surface of the earth and as a place to live for species of living things.
4. Where weather and climate events occur, eg rain, wind, lightning, and clouds.
5. There is a tropopause layer, which is the layer between the troposphere and the stratosphere.
For each increase 100 meter, the temperature drops 0,5 to 0,6 ° C.
Characteristics of the Thermosphere:
Stands about 80-800 km.
This layer is often referred to as the hot layer.
The air temperature at the top of this layer can reach> 1000 ° C.
There is also an ionosphere layer in this layer.
The ionosphere layer functions to spread radio waves

Such is our explanation of Matter Layers of the Atmosphere and Their Explanation. Hopefully with this article, Yuksinau.co.id friends, increase his knowledge about knowledge Geography. Read Also Indonesian map. thank you for visiting.
The post Lapisan Atmosfer appeared first on YukSinau.co.id.
