Myelin sheath function
Myelin sheath function – In nerve cells, The myelin sheath is a phospholipid layer that concentrically wraps around the axon. For more details, you can refer to our explanation of the biology/IPA material about the myelin sheath, starting from the definition of, function, complete structure with picture below.
Table of Contents
Definition of myelin sheath
In nerve cells, The myelin sheath is a phospholipid layer that concentrically wraps around the axon. Schwann cells are cells that form the sheath in the peripheral nervous system, whereas oligodendrocytes are cells that form a similar sheath in the central nervous system.
The myelin sheath is a feature of vertebrates (gnathostoma), but sheaths such as myelin have also developed in parallel with some invertebrates.
myelin sheath (neurolemma) is a layer of Schwann cells that has a nucleus and cytoplasm covering the axons in nerve cells. Myelin sheath is an insulating material, that is, it cannot give an impulse (stimulus).
The function of myelin is likened to wrapping a cable, while the copper wire is the axon. Here is a more complete function of the myelin sheath
Myelin sheath function
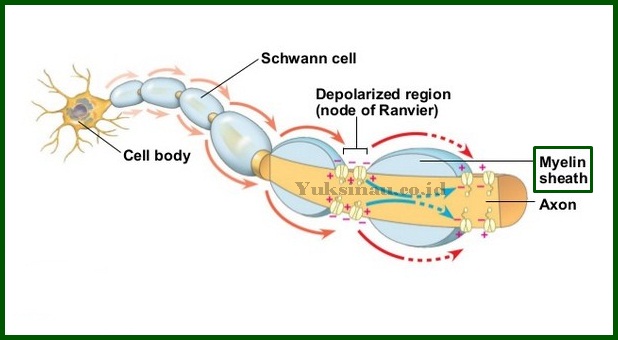
The main function of the myelin sheath is to protect and insulate the axon and enhance the transmission of electrical impulses both. When myelin is damaged, the transmission of these impulses will automatically slow down and occur in severe neurological conditions such as multiple sclerosis.
The main purpose of myelin is to cover neuron cells so that they can carry out action potentials more quickly.
The function of the myelin sheath is to facilitate the transmission of electrical impulses through the nerve cells. The myelin sheath consists of a modified plasma membrane that rotates around the nerve axons.
The myelin sheath is essential for the proper functioning of the nervous system. When myelin is damaged, nerve impulses slow down and nerve cells begin to wither. Diseases such as multiple sclerosis can be caused by damaged myelin sheaths.
The sheath increases the electrical resistance of the cell by a factor 5.000, thereby preventing the electric current from leaving the axons of the nerve cells. The process of forming the myelin sheath is called myelination.
Myelin production begins at the 14th week of fetal development, but at birth, very little myelin found in the brain. In childhood, Myelination occurs rapidly and continues until puberty. The myelin sheath is composed of lipids and proteins, and lipids store approx 70 to 80 percent of the sheath structure.
So from the explanation of the function above, we can conclude that this myelin sheath has several functions as follows :
- As axon protector.
- Facilitates impulse conduction.
- As axon growth medium when axon is damaged.
- Increase impulse speed. Impulses will jump over the myelin sheath with speed 120 meters/second.
- Increase electrical resistance, thereby preventing impulses from flowing out of the axon.
- Provides nutrition to the axon.
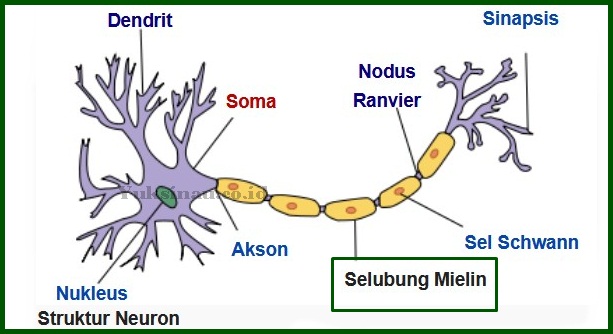
Meilin Sheath Structure
If you look at the picture above, the myelin sheath is like a series of sausages that surround the axon. There is a gap between the myelin sheath which is approx 1 millimeter. This gap is called Nodus Ranvier.
In the myelin sheath there are what are called Schwann cells (a glial cell in the peripheral nervous system). The fat in the myelin sheath serves to protect the axon from electrically charged atoms and molecules.
Therefore, The myelin sheath is an insulator. The myelin sheath makes the white matter in the brain whitish.
F.A.Q
Dendrites have a function as a sender of impulses to the nerve cell body, whereas the axon's function is to send impulses from the cell body to other tissues.
The function of synapses is to provide connections between neurons that will allow impulses to flow between them (synapses and neurons).
The function of Schwann cells is to accelerate impulses (stimulus) to 10 times with just a little energy. Also acts as a regeneration process in the damaged peripheral nervous system. dll.
That's what we're talking about Myelin sheath function. You can also study some of our articles related to Biology/Science lessons below.
Related article :
- Function of the Golgi Body
- Vacuole Function
- Cell Wall Function
- Chromoplast Function
- Centrosome function
The post Fungsi Selubung Mielin appeared first on YukSinau.co.id.
