Heart Function
Heart Function – The heart is an organ of the human body that has a cavity and is muscular which plays a role in the human circulatory system. The main function of the heart is to pump blood throughout the body.
Table of Contents
Definition of the Heart
The heart is an organ of the human body that has a cavity and is muscular which plays a role in the human circulatory system.
The heart controls all activities of blood circulation, by connecting the blood vessels that become the channel.
The heart then pumps blood throughout the body through rhythmic contractions with the help of the heart's electricity. which is then pumped blood throughout the body.
The content in the blood is nutrients and oxygen which are useful for the survival of cells in the body.
Then, when used by the cells, the blood returns to the heart, and so on.
Heart Function
The function of the heart is as a means of transportation in the body, Blood is responsible for carrying the nutrients and oxygen needed by other organs of the body.
The main function of the heart is to pump blood throughout the body.
Heart & blood vessels then form the cardiovascular system to ensure the survival of living things.
In a normal or healthy heart, it is supported by strong muscle tissue and works well in the process of pumping blood.
The heart that beats continuously in pumping blood, will drain over 14.000 L of blood in one day.
Parts of the Heart and Their Functions
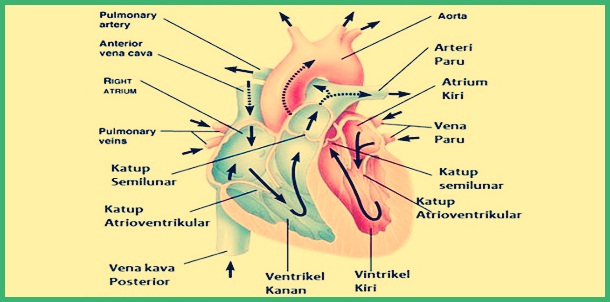
The heart has parts where each part has its own role, The following is a complete explanation ;
1. Right porch
Right porch, which in this part there is dirty blood. Dirty blood is blood that has very little oxygen, enters the right atrium through the superior vena cava & inferior.
From the right atrium, then the blood will be pumped to the right chamber. On the fetal heart, there is an opening in the right atrium that allows blood to flow directly into the left atrium.
Where this is very important for fetal circulation, because the fetus's lungs have not been able to work properly, so that the fetus will take clean blood rich in oxygen directly from the mother.
After birth, baby's lungs will expand and begin to function. The hole will then close and create a boundary between the right atrium and the left atrium.
The conclusion, The anatomical function of this part of the heart is to receive dirty blood from the body which will then be carried by the blood vessels.
2. Right room
The right ventricle is a safe part, this part has the role of pumping dirty blood to the lungs so that carbon dioxide can be exchanged for oxygen through the breathing process.
This right room is under the right porch and next to the left room. Dirty blood flowing through the right atrium will pass through the tricuspid valve.
Then this blood will be pumped into the lungs through the pulmonary valve and travel through the pulmonary arteries.
If this part does not work well, so it can no longer pump efficiently, this is the reason people experience right heart failure.
3. Left atrium
In this section which has a function as a recipient of clean blood coming from the lungs.
Clean blood is blood that contains good oxygen. Clean blood enters the left atrium via the pulmonary vein or vein
Then, This blood is pumped into the left ventricle through the mitral valve. The porch has thinner walls and is not as muscular, according to its role, namely only as a blood receiving room.
4. Left room
Left chamber of the heart, which is located below the left atrium separated by the mitral valve.
The left ventricle is also the thickest part of the heart whose role is to pump clean blood throughout the body.
The condition of high blood pressure can cause the left ventricle muscles to enlarge and then harden, because of the increased workload of the left ventricle of the heart in pumping blood.
When this happens continuously, then the function of the heart in this part in pumping blood throughout the body will be disrupted.
Heart Structure and Functions
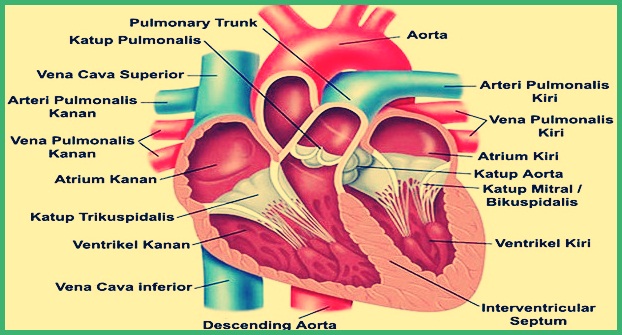
The heart is divided into 2 cavity (left cavity & right cavity) by a muscular wall called the septum. The septum itself is a barrier that separates a cavity.
The two cavities consist of two chambers each, The upper chambers are called atria and the lower chambers are called ventricles.
Where the right cavity receives de-oxygenated blood from various parts of the body (except the lungs) and then pump it into the lungs.
While the left cavity receives oxygenated blood from the lungs, which will be pumped throughout the body.
About the complete structure of the heart, We will discuss this in detail here :
| Heart Structure | function |
| Aorta | Carrying oxygenated blood to all parts of the body in systemic circulation. |
| Pulmonary Artery | Carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle of the heart to the lungs. |
| Pulmonary Vein | Carries oxygen-rich blood back to the heart and then circulates throughout the body. |
| Atrium | Receives oxygen-rich blood from the lungs and carries it to the left ventricle. |
| Vena Kava Superior | Brings back carbon dioxide rich blood from all over the upper body to the heart. |
| Ventricle | Receives blood from the left atrium and carries it throughout the body. |
| Mitral Valve | Prevents blood that has been in the left ventricle from returning to the left atrium |
| Canine valve | Keeps blood flowing only from the atria to the ventricles, thereby allowing blood to flow in its place. |
| Heart Wall | To protect the inner lining of the heart |
| Pericardium | As the outer wall of the heart. |
How the Heart Works
The function of the heart in the pumping process and as a supplier of blood throughout the body is not simple.
The right atrium receives blood from the rest of the body through the vena cava, which then flows into the right ventricle.
Vena Kava itself is the main vein in the body that carries blood that contains lots of carbon dioxide from the head and lower body organs to the right atrium
Blood from the right ventricle is then pumped out of the heart to the lungs, to exchange carbon dioxide for oxygen.
Blood that has been filled with oxygen, then it will be pumped into the left atrium, then to the left ventricle, which will flow throughout the body through the aorta.
In order for the blood to flow properly and precisely, the heart has valves. Which valves help blood flow from the atria to the ventricles are the mitral and tricuspid valves.
The valves that control the flow of blood leaving the heart are the aortic valve and pulmonary valve.
Of the 4 valves will keep the blood moving forward in one direction. The valves close quickly to prevent blood from flowing backwards.
Types of Heart Valves
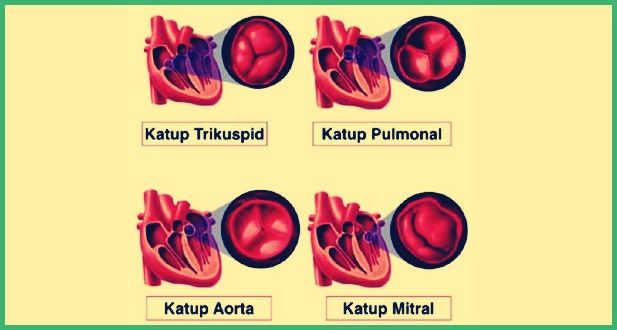
There is 4 a type of heart valve whose function is to keep blood moving forward in one direction.
The valves close quickly to prevent blood from flowing backwards. The following are the types of valves in the heart and their functions :
| No | Valve Type | function |
| 1 | tricuspid valve | Regulates blood flow between the right atrium and right ventricle. |
| 2 | Pulmonary valve | Regulates blood flow from the right ventricle to the pulmonary arteries which carry blood to the lungs to pick up oxygen. |
| 3 | Mitral valve | Flows oxygen-rich blood from the lungs flowing from the left atrium to the left ventricle. |
| 4 | aortic valve | Opens the way for oxygen-rich blood to pass from the left ventricle to the aorta. |
The main function of the heart is to pump blood throughout the body.
1. tricuspid valve
2. Pulmonary valve
3. Mitral valve
4. aortic valve
1. Right porch
2. Right room
3. Left atrium
4. Bilick is a snowflake
Thus, Yuksinau.co.id's discussion of heart function paper material includes understanding, structure, type, parts of the heart and their functions. May be useful.
Other Articles :
- Southeast Asia Map
- World map
- Indonesian map
The post Fungsi Jantung appeared first on YukSinau.co.id.
