Functions of Plant Cell Walls
What is the function of the cell wall in plant cells?? The cell wall in plants is a rigid layer, which this cell wall surrounds some of the cell types. For more details, see the Paper on the Functions of the Cell Wall in Plant Cells, Definition, Features, Type, Structure, and Full Picture below.
Table of Contents
Definition of Cell Wall
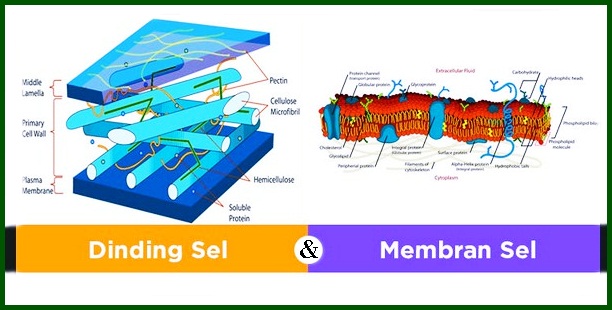
The cell wall in plants is a rigid layer, where the cell wall surrounds some types of cells.
This area is located on the outside of the cell membrane which is responsible for providing strength, clerk, and protection against mechanical stress as well as infection.
other than that, This cell wall provides the cell with limited plasticity but plays a role in preventing the cell from bursting due to turgor pressure.
What is turgor pressure? turgor pressure is the pressure that pushes the cell membrane against the cell wall found in plants
Cutin-coated cell walls prevent water loss and also help in communication between cells.
The cell wall is characteristic / plant cell characteristics, bacteria, fungi / mold, algae and some archaea. Protozoa as well as animals do not have cell walls.
As for types of plant cells that is ;
1. parenchyma cells,
2. Collenchyma cells,
3. Sclerenchyma cells,
4. Xylem cells,
5. Phloem cells,
6. Sel epidermis
Cell Wall Functions in Plants
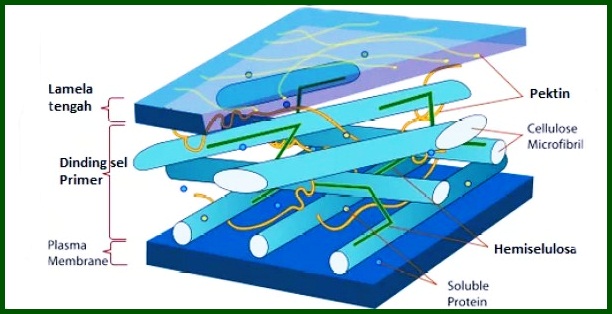
Of course, this cell wall has a very vital function for plants. Then, What is the function of the cell wall in plant cells??. Following are the functions of the cell wall in plant cells: ;
The main function of the cell wall : give stiffness, strength,and structural support, and provides protection against mechanical stress as well as infection.
1. Protect Cells
The function of the cell wall in plants is to play a role in protecting the inside of the cell from environmental influences from outside the cell, and also helps in the diffusion of gases into and out of the cell.
2. Withstand Pressure
The function of the cell wall is to withstand excess pressure when water enters the cell. As for the impact of excessive pressure, the inside of the cell will be disturbed.
3. Gives Cell Shape
The function of the cell wall is to give shape to the cell. The shape of plant cells will be awakened, and this is because of the cell wall itself.
4. As a cell filter
The cell wall in plants acts as a filter / filter against cells. Large molecules that come from this environment will be filtered by the cell wall so as not to enter the cell.
5. Regulating the entry and exit of substances
The cell walls of plants, functions in regulating the entry and exit of substances in the cell. This function is the same as the function of the cell membrane.
In addition to the above functions, This cell wall also has other functions, which we will present in the table, For that, see the table below :
Cell Wall Function :
| 1 | Provides mechanical strength |
| 2 | Withstand turgor pressure |
| 3 | Protect cells from mechanical stress |
| 4 | Maintain cell homeostasis |
| 5 | Helps the process of diffusion through the apoplast |
| 6 | Carbohydrate storage |
| 7 | As a hormone, because the cell wall contains oligosaccharin |
| 8 | Has semipermeable properties, so that only certain substances can enter the cell |
| 9 | Place of exchange, proteins and small molecules that enter and leave the cell |
| 10 | The rigid nature of the cell helps the plant to stand upright and prevents the entry of pathogens |
Read Also : Centrosome function
Characteristics of Plant Cell Walls
After we see the explanation above, we can conclude that the cell wall in this plant has characteristics or characteristics. Then what are the characteristics of the cell wall??
- The cell wall is thin but multi-layered.
- The base layer formed during cell division is pectin, which is a substance that makes gelatin thicken. The function of this layer is to glue adjacent cells.
- After cell division, new cells will form an inner wall derived from cellulose fibers, This wall will stretch as the cell grows and will also become thick and then stiffen as the plant matures.
Plant Cell Wall Structure
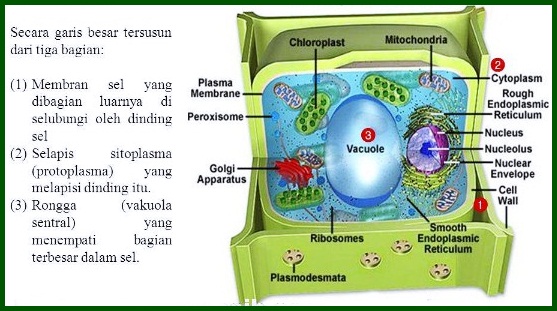
The cell wall in plants consists of several parts or very complex structures, The cell wall structure consists of three parts:, the primary cell wall, secondary cell wall, and tertiary cell walls.
So what is the primary cell wall?, seconds, and tertiary?. Check out the explanation below regarding the parts of the cell wall;
Read Also : Vacuole Function
1. Primary Cell Wall
Primary cell wall, is the cell wall in parenchyma cells, Cells that are actively dividing are called embryonic, or young cells.
The primary cell wall in its formation will be accompanied by the formation of a secondary cell wall that will lead to the inside of the cell.
The characteristic of this primary cell wall is that it has a thickness of 0,1 to 0,2 micron. This primary cell wall also contains a network of cellulose microfibrils surrounding the secondary cell wall.
2. Secondary Cell Wall
Secondary cell wall, where this cell wall has a greater thickness than the primary cell wall. The secondary cell wall is composed of tightly packed cellulose microfibrils.
Besides cellulose, This secondary cell wall contains lignin fibers, i.e. plant components that are located between the cellulose microfibrils.
3. Tertiary Cell Wall
The tertiary cell wall is on the inside of the secondary cell wall. This tertiary cell wall is different, with primary and secondary cell walls.
Between the cell wall and other cell walls have pectin substances located in the middle lamella / middle lamella, which is the layer that cements the cell wall 2 adjoining plant cells
Between one cell and another there is a protoplasm bridge or link called plasmodesmata. Plasmodesmata play an important role in the transportation of various substances between cells.
The cell wall in plants is a rigid layer, which this cell wall surrounds several types of cells.
This area is located on the outside of the cell membrane which is responsible for providing strength, clerk, and protection against mechanical stress as well as infection.
Turgor pressure is the pressure that pushes the cell membrane against the cell wall found in plants
Cutin-coated cell walls prevent water loss and also help in communication between cells.
The cell wall is characteristic / plant cell characteristics, bacteria, fungi / mushrooms, algae and some archaea. Protozoa as well as animals do not have cell walls.
1. Primary Cell Wall
2. Secondary Cell Wall
3. Tertiary Cell Wall
Thus our discussion of the Paper Material Cell Wall Functions in Plant Cells Complete. Read it too Heart Function Complete. thank you for visiting.
The post Fungsi Dinding Sel Tumbuhan appeared first on YukSinau.co.id.
